Dr. Minh Huy Do
Rosuvastatin belongs to a class of medicine used to reduce “bad” cholesterol levels in human beings’ bodies, and it is being manufactured more and more to serve medical purposes. Electrochemical methods perform high potential of application in controlling the quantity of rosuvastatin during the production process and even in commercial drug tablets that are available in many drugstores due to their ability to give a fast analytical performance and relatively low price. In this study, we report an electrochemical determination of rosuvastatin at activated glassy carbon electrode using differential pulse voltammogram. The measured parameters for the quantification of rosuvastatin, i.e. accumulation time, pH, and supporting electrolyte were optimised. Under the optimised conditions, the electrochemical method for rosuvastatin detection archived the linear range from 0.15 mg L-1 to 2.5 mg L-1. Limit of detection and limit of quantification were estimated as 0.035 mg L-1 and 0.12 mg L-1, respectively. The difference in the content of rosuvastatin in commercial drug samples between the analytical results obtained by this electrochemical method and the published values of the manufacturer was 0.10 % ÷ 1.10 %, and the recovery varied between 98.6 % and 101.1 %. This method was then compared with HPLC-UV as an arbitration method, and our results showed a difference of 0.10 % ÷ 1.10 % in the amount of RSV.
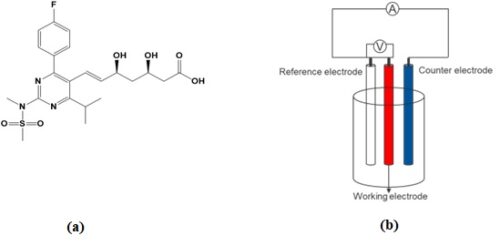
(a) The chemical formula of rosuvastatin, and (b) Three electrode system








